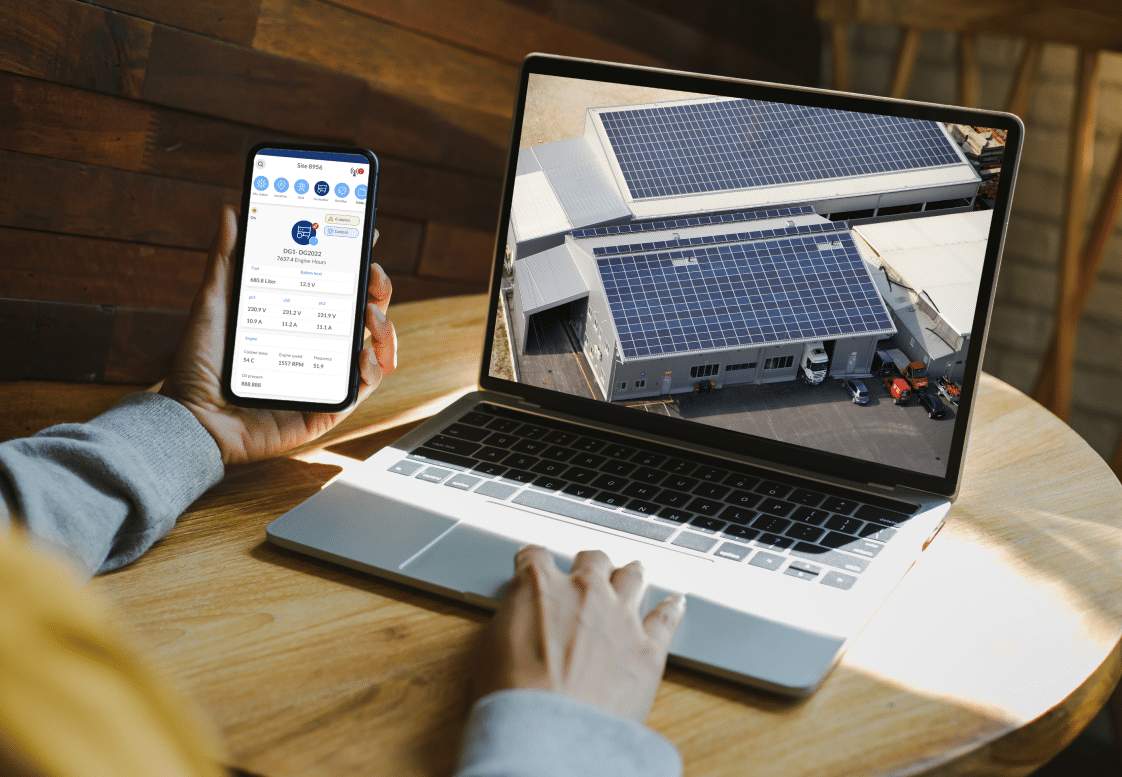
Did you know residential and commercial buildings comprise nearly 60% of the world’s electricity consumption? Including over one-third of greenhouse gas emissions?
Moreover, these numbers are growing at a rapid rate. To lower greenhouse gasses and to prevent the threat of climate change, smart buildings and available technologies are needed more than ever before.
By 2030, the smart buildings sector is expected to reach $78.2 billion, doubling from 2022. Over 115 million smart buildings will be complete and in use by 2026.
Let’s look at what smart building technologies are and why they’re proving vital in 2022.
What are smart building technologies?
Smart building technologies are any IoT-based solutions, including software, hardware, and connectivity used to remotely monitor and manage energy, HVAC, lighting, and security assets.
Unlike traditional building management, which requires onsite visits to diagnose and remedy issues, these innovations provide organizations an intuitive look into their building operations from afar.
Most smart buildings are designed from the ground up, with digital systems that can collect raw data and organize it to track trends and identify potential malfunctions.
These systems drastically improve energy and utility efficiency while reducing wasteful or unnecessary usage and carbon emissions.
How do smart building technologies improve efficiency?
Knowledge is power, but most buildings are still stuck running on an analog system where insights can only be discovered by physically inspecting each individual asset. This leaves ample room for inefficiencies, wasted energy and cooling, and needless carbon emissions.
Introducing smart building technologies like clean energy-based heating pumps could reduce carbon emissions by 9% annually.
Efficiency-optimized smart buildings are estimated to save around $18 billion in energy costs and 80 million tons of CO2 by 2030.
It’s not just the carbon emissions and costs that are lowered with the introduction of smart building technologies; they also:
- Provide in-depth insights into energy, utility, and HVAC usage
- Help quickly identify potential malfunctions or areas for optimization
- Provide actionable insights into operations to help make data-driven decisions based on live usage
- Automate many analog processes making management more straightforward and effective
- Deliver significantly more accurate usage tracking and identify places for improving operations
Smart building technologies improve building managers’ visibility, provide insights into which assets need to be optimized, and can determine why malfunctions occur.
By actively monitoring energy assets and other machinery, these issues can be detected as they happen, and alerts sent to relevant stakeholders to mitigate the problem.
These technologies help with accurate billing when multiple tenants are involved, as smart meters can streamline the billing process, ensuring tenants pay correctly with usage attributed to the correct unit.
9 Smart Building Technologies for Optimal Energy Usage
With the importance of smart building technologies for efficiency and conscious energy use out of the way, let’s look at some of the best technologies and solutions to help you achieve these goals.
1. Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) relates to any network-connected technologies that help analog assets provide data and insights into their operations. From light bulbs to generators to entire buildings, IoT technologies are an inseparable element of any smart building.
Without this connectivity, there would be no way to accurately track various assets’ performance and tenants’ utility usage nor mitigate potential malfunctions without being onsite.
IoT solutions simplify a wide variety of traditionally hands-on tasks that saves building managers time and money while helping them maintain access and visibility over their buildings and assets.
2. Smart Sensors
An integral part of IoT technologies is smart sensors which connect with remote assets and sites to retrieve information to be organized and analyzed. From asset monitoring to remote access and security controls, smart sensors provide a litany of functionalities that streamline building management.
Smart sensors can help accurately track colocated tenants’ utility usage and even determine the health and stability of the building itself.
3. Remote Monitoring Solutions
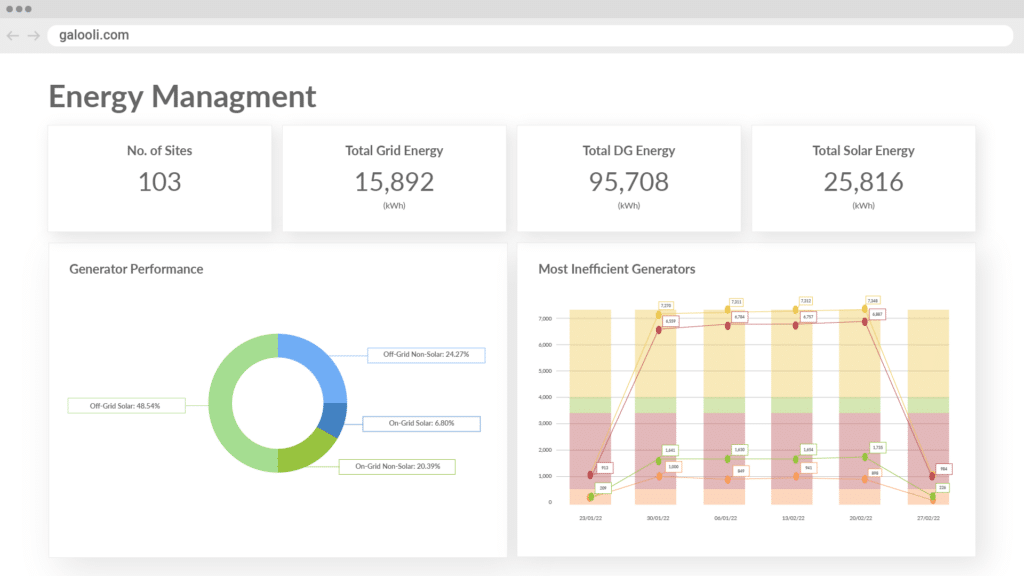
All the technology and connectivity in the world won’t make a difference to your bottom line if you have no way to actively monitor your building(s) and assets.
Remote monitoring solutions like Galooli provide overarching visibility while establishing performance thresholds attached to alerts whenever they are crossed.
This lowers costs as work can be done away from the site, saving on resources and contractors. It’s particularly beneficial for those with hard-to-reach locations.
4. Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are transforming organizations’ capabilities to delve into their operations to detect trends and areas for improvement on all levels.
These algorithms take insights one step further by considering potential scenarios or future issues that could arise and provide the alert needed to remedy or address them ahead of time.
AI is an intrinsic part of building a “digital twin” of your buildings, using mass quantities of data to develop a digital model to run scenarios and simulations to optimize operations further.
5. Aerial Drones

Another challenge to successful business management is accessibility. Some issues cannot be easily or safely reached by managers or technical and maintenance staff and require machines or remote platforms to diagnose and even remedy such situations.
Fortunately, aerial drones have grown beyond cinematography and hobbyists and can be deployed in industrial and commercial applications. Beyond identifying and gathering information, drones can be used for security and surveillance and connected to a phone to track footage in real-time and examine data feeds.
6. Lighting
Modern advanced lighting controls use nearly 45% less energy than their analog counterparts.
With smart lighting solutions, they can keep track of room occupancy, locate items quickly, and track power consumption.
Smart lighting can also take variables, like available natural light, and adjust for certain times of day, like waking up and going to sleep.
7. Ultra-efficient Heat Pumps
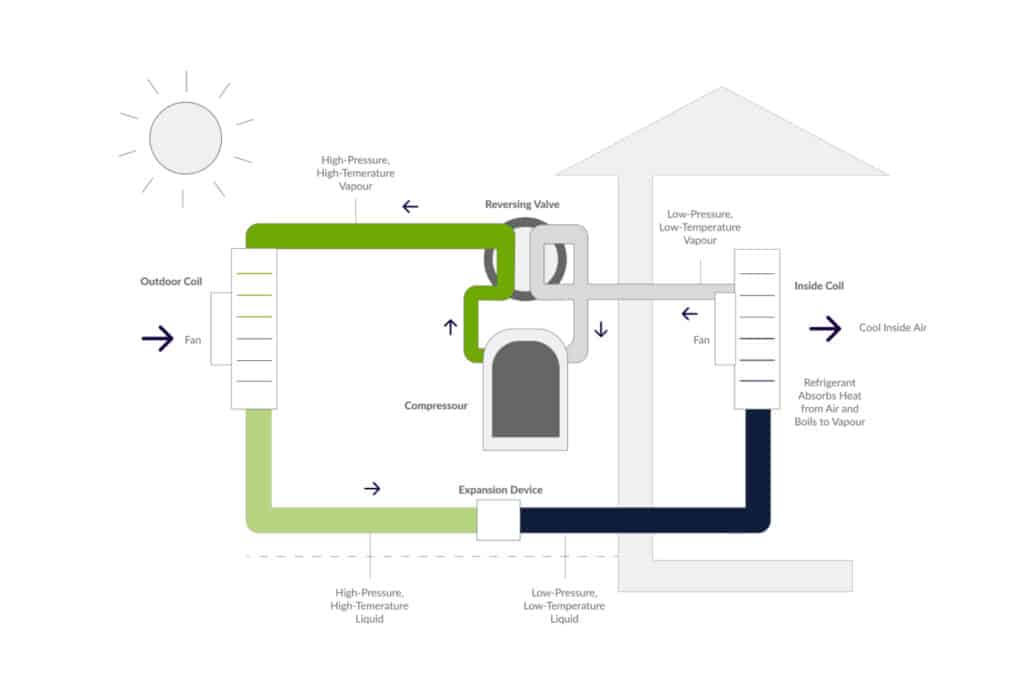
Heat pump systems are a relative newcomer to the HVAC sector and have replaced traditional fossil-fuel-reliant heating and cooling systems with smart, electrified heating and cooling. They can move around liquid refrigerants or heat to where it is needed, and through this, energy consumption can be reduced by 50% compared to conventional HVACs.
These efficiency-first pumps help building managers maintain temperature controls on a room-by-room basis, with the ability to change each on demand.
When integrated with AI modeling, these pumps can use historical and live data to predict heating and cooling use and automatically adjust the temperature accordingly.
8. Plug Loads
Buildings must have the electric flexibility to power and handle multiple types of equipment throughout the building. From laptops and phone chargers to office equipment and building infrastructure, each device has its own energy requirements that must be met.
Smart plug load controllers can access any and all sensors related to energy use and load and cut power to any devices or machinery running unnecessarily.
Introducing smart plug load sensors can reduce related energy consumption and some can even detect secondary connected devices, like in the case of devices connected via UPS or power strip.
9. Reflective Roofing
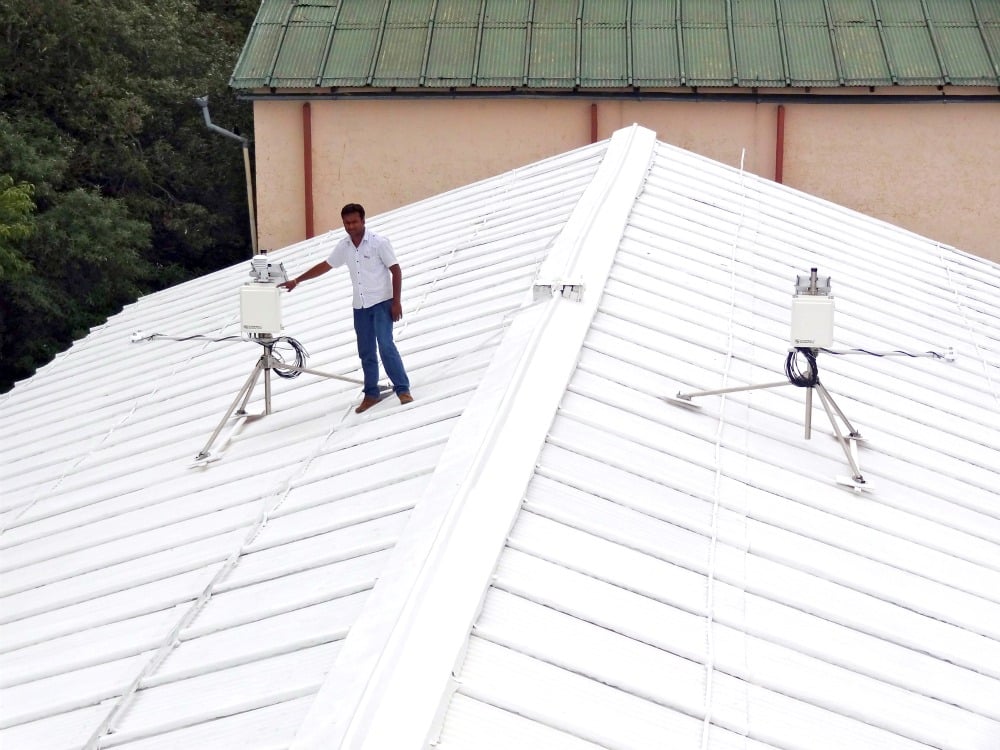

Roofing may seem like a redundant space in smart tech, but not anymore.
Traditionally, roofs are sealed with tar or similar compound that seals the building from the elements. But, that sealant also absorbs a great deal of sunlight, and that thermal energy needs to be dispersed.
Cool roofs are metal coated with materials containing pigments that reflect sunlight and absorb significantly less heat than regular roofs. This, in turn, lowers the overall temperature of the building and reduces the need for additional HVAC and overall energy usage.
In addition, buildings are installing solar panels on their roofs to harness, instead of absorbing or reflecting solar energy.
Take back control of your building’s operations
Buildings are getting smarter, and managers would do well to hop on the trend and start integrating intelligent building technologies into their operations plan.
Though the world is still heavily reliant on older, unoptimized buildings, smart buildings are trending upward as we become a much more digitally connected world.
The potential to minimize wasted energy while improving building energy efficiency and carbon footprint is enormous, with many innovations focused on achieving this.
Along with creating a more customized and responsive experience for managers, these technologies will remove the need for onsite visits, automate analog processes, and save on operations and energy costs.If you want to transform your building operations while eliminating wasted energy, learn more here.
Connect With Us
operational cost savings & efficiency?