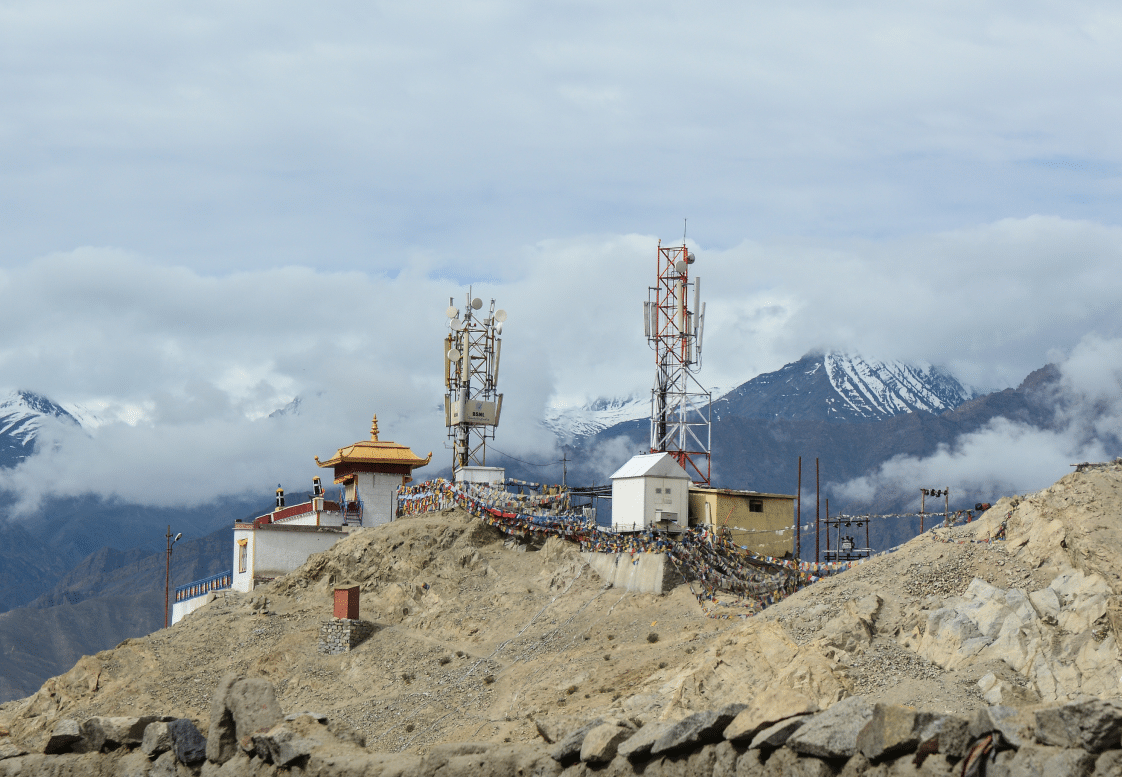
With every passing year, we become more reliant on technology that runs on electrical power. Whether it’s medical equipment that allows doctors to save lives or the charging of electric cars to help people get around, the need for reliable power is evident.
In crises where the power goes out, our reliance on it can prove to be deadly. Businesses and communities worldwide are increasingly finding microgrids as the go-to answer for sustainable and dependable power.
A central grid can efficiently light up a dense urban area, but the world isn’t just made up of cities. Across the globe, more than 770 million people are living without access to electricity. Even in areas generally well-served by central grids, vulnerabilities within the infrastructure can suddenly plunge millions of people into darkness.
Whether you’re looking to provide power to a remote location or ensure uninterrupted electrical output when disasters strike, microgrids quickly become one of the most cost-effective solutions. Let’s look at how microgrids are reshaping the energy industry and share tips on getting the most out of a microgrid energy system.
What are Microgrids?
A microgrid is essentially just a smaller version of a central power grid, but they generate and store energy independently. They can be used in numerous situations, including medical centers, tribal settlements, industrial facilities, schools, corporate offices, electric vehicle charging, and sustainable communities.
Microgrids are often used as backup power sources, but they can also operate independently as the sole power source for anything from a single residence to a large site consisting of multiple structures.
How do Microgrids operate?
Microgrids operate differently depending on how they are designed and what purpose they are intended to serve.
An ‘island’ or off-grid microgrid is designed to operate independently without connection to any upstream power sources. They rely solely on their own distributed energy resources to generate power. This is a huge attraction for sites that are cut off from central grids due to their remoteness (or because they are, in fact, islands.)
Grid-connected microgrids remain connected to a central grid and are typically used to provide backup power during emergencies, outages, or periods of high demand. They can also draw power from the central grid and generate their own supply.
The essential elements of a microgrid consist of the following:
- Distributed energy resources like diesel or natural gas-powered generators, fuel cells, wind turbines, or solar panels
- Batteries for storing energy
- Load management systems to distribute power based on demand
Microgrids benefit heavily from remote control and communication systems that can monitor and address problems around the clock.
What problems do microgrids solve?
Microgrids can address several problems all at once. They provide power to remote and hard-to-reach areas, allowing more people to access that much-needed resource.
They also serve as an additional source when the central grid goes down, which happens more often than you’d like to imagine. Over the past 50 years, there has been a fivefold increase in weather-related natural disasters. These incidents, like storms or wildfires, can cause equipment failure at critical points in a central grid system, causing a complete central grid blackout.
This is where microgrids can save the day, as organizations can lose millions of dollars in an outage – or even worse for hospitals, government offices, and essential industries that require consistency at all times.
And as we enter into 2023, with sustainability being a driving force across various industries, microgrids are suitable for those looking at renewable energy sources. For example, there are solar stations designed to power electric vehicles via microgrids.
In addition, businesses and communities can have much greater control over where their energy comes from and how they manage it when utilizing microgrids. They can be built in areas the central grid won’t reach, and they can be made to use energy assets like wind and solar that emit less carbon into the atmosphere.
How to get the most out of your microgrids?
Right now, there are more than 4,475 microgrid projects in the world. With the number expected to rise due to the increasing need for the benefits microgrids provide.
The entire development cycle for installing a microgrid runs between 18 and 36 months. While microgrids are becoming more affordable, they still represent a significant investment, and it’s important to think carefully about maximizing their potential from the very outset.
You’ll want to consider the location of the microgrid and the energy consumption habits of the organization or community that will be using the microgrid and select energy assets that will meet the requirements of both the expected demand and the conditions on the ground. It’s also important to weigh your financing options, ensure you have all of the necessary permits and approvals and plan for the possibility that you might need to scale your microgrid up at a future date.
To build a robust and scalable microgrid, you’ll need to choose the right equipment and solutions to help you monitor, maintain, and protect it. Remote management tools can help you balance energy loads, maintain optimal operating temperatures, and monitor system performance to detect issues early on. This will improve your overall energy efficiency and extend the life of your equipment.
6 ways microgrids are reshaping the energy industry
For varied groups of end users, microgrids represent the future of energy production. Here are six of the biggest impacts microgrids are having on the global energy industry:
1. Microgrids offer a more sustainable option
Organizations are increasingly using renewable energy sources to power their microgrids: wind, solar, and hydro. These sustainable options significantly reduce your carbon emissions compared to generators that burn fossil fuel, and the energy they produce can be stored in batteries for use on demand.
Going green is a high-priority goal for many organizations, and microgrids are one of the most effective ways to generate sustainable power, increasing energy efficiency by as much as 60%.
2. Microgrids can operate autonomously
While many microgrids are designed to run off the central grid when possible, they always have the option of switching to ‘island’ mode when demand gets too high or when disasters and other unforeseen events cause power outages. For businesses, this means avoiding costly downtime, but for hospitals and other organizations that provide critical services during times of crisis, microgrid power can literally save lives.
3. Microgrids provide power options for remote locations
Obtaining central grid power in remote or isolated areas can be very expensive or even impossible. When microgrids are on the table, any business facility or residential area can implement an affordable, localized energy solution designed to meet their unique requirements. Thanks to microgrids, communities in developing countries that never had access to regular power can now generate their own electricity 24/7.
4. Microgrids provide resilient energy sources
Microgrids can be designed to be far more resilient than the power distribution systems that run off a central grid. The equipment, energy assets, and control systems can all be set up and configured to optimize efficiency, balance loads during peak usage hours, and endure harsh external conditions.
Remote monitoring solutions can be employed to ensure all performance standards are being met and that necessary maintenance is carried out on time, minimizing the risk of unexpected downtime.
5. Microgrids are more secure
Energy assets are subject to theft, vandalism, cyberattacks, and other forms of tampering. Few utility providers can afford to secure every vulnerable element of a large central grid, but microgrids can be hardened as needed with physical security measures, electronic defenses, and remote monitoring.
6. Microgrids are beneficial in areas with extreme weather or natural disasters
Microgrids can provide power when storms, wildfires, and other disasters knock out the central grid. They can be designed to withstand extreme weather and remain operational during even the most difficult conditions. When you know that a microgrid will operate in an area subject to these events, you can protect it with a reinforced structure and include additional generator capacity.
Step into the future with microgrids
Nobody wants to see a future where everyone has to depend on fuel-burning power plants doling out energy across an aging, vulnerable grid infrastructure. Microgrids give businesses and communities the power to take control of their own energy needs, generating electricity through sustainable resources of their choosing.
The key to making microgrids work efficiently is supporting them with the right technological solutions. Remote monitoring tools like Galooli provide real-time visibility into microgrid systems, helping operators optimize performance and address potential issues proactively. Book a demo and find out how Galooli can unlock the full potential of your microgrid.